In order to avoid most problems with your pool water, it is imperative to keep it balanced. Along with sanitization, water balance is the most important thing you can do as a pool owner. The science behind it may seem daunting, which is why Pinch A Penny developed the Pool House to make it easier to understand. The Pool House is a graphic representation of the elements that make up your pool’s water, and it was designed to educate pool owners about chemistry and water balance.
A balanced swimming pool means keeping the five basic pool water components (total alkalinity, pH, chlorine, calcium hardness and stabilizer) within their proper levels. Each level builds on and effects the other, and these components work together to help the sanitizer work more effectively. This is why we recommend that you test your water weekly at your local Pinch A Penny store or in the app.
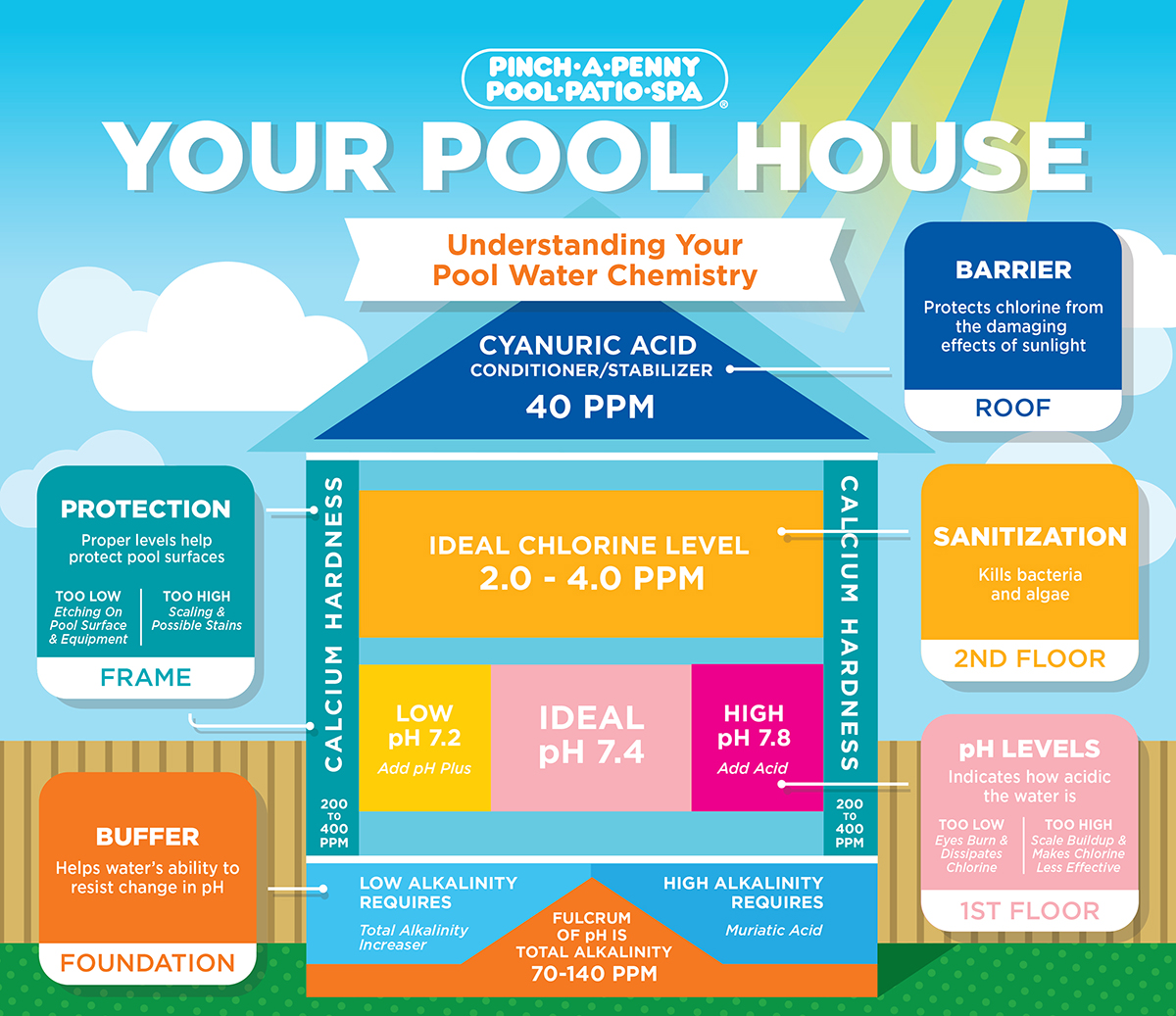
Total Alkalinity
The foundation of your pool chemistry is total alkalinity. This acts as a buffer to help the water’s ability to resist changes in pH. The two influence one another, and we often say that total alkalinity is the fulcrum of pH. Low alkaline water leads to low pH and high alkaline water leads to high pH. A pool should have a total alkalinity level between 70-140 ppm (parts per million).
pH Level
pH refers to the pool’s acidity or baseness and is considered the first floor of the house. Keeping your pH levels within the proper range is important for swimmer comfort. It also helps to keep the equipment and finish in good condition. A proper pH level is in the range of 7.2 to 7.8, with the ideal being 7.4. You can adjust pH levels by adding pH Plus or pH Minus.
Chlorine Level
The second story of your pool house is the chlorine level. This is the sanitizer in your pool which kills algae and bacteria. The ideal levels for chlorine are 2.0-4.0 ppm. We have articles on our blog about the importance of chlorine.
Calcium Hardness
We refer to calcium hardness as the walls or frame of the pool house. The right amount of calcium in pool water is crucial to protect your pool’s surfaces. Too little and your pool's surface can begin "chalking" and erode. Too much and your water could become murky, scale formations could appear, and stains might begin to form. 200 to 400 ppm is the general range for calcium hardness levels.
Stabilizer
We call cyanuric acid, or stabilizer, the roof because it protects the chemicals in your water from the sun and helps your pool retain chlorine longer. Stabilizer is added to some types of chlorine to protect it from breaking down due to the harmful effects of U.V. rays. When your stabilizer level is low, you'll go through a lot more chlorine than normal. You can bring the levels up by adding Stabilizer/Conditioner. When it's high, you may need to dilute your pool water to bring it back into the normal stabilizer range, which is 40 ppm.
Share This Post

